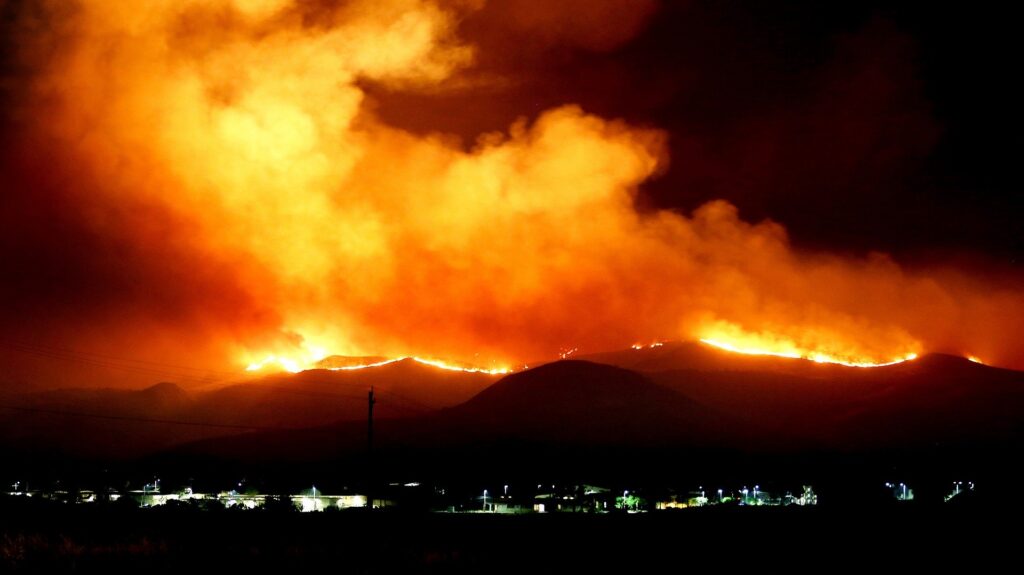
Over the past few weeks, wildfires have raged from Washington to California, devastating communities and causing extensive damage. Climate change is being pointed to as the driving force behind the fires – hot, dry conditions throughout the West provide acres of fuel for the blazes. But what is sparking these deadly wildfires? What can California, specifically, do to decrease the number of wildfires each season? In this article, we’ll explore why power lines are to blame for many of the fires and how an increase in energy storage could help lower fire risk.
How Power Lines Start Fires
There are a number of ways power lines can lead to fires. Wind can blow nearby trees and branches into power lines or snap wooden distribution line poles, causing live wires to fall onto dry grass. While such problems exist in a number of states, the most serious problems have occurred in California, especially over the last two years.
A report by the California Department of Forestry and Fire Protection noted that California’s 2017 Redwood and Atlas fires started when trees and branches came into contact with power lines. The Redwood Fire burned more than 36,000 acres, demolished 543 buildings, and killed nine people. The Atlas Fire burned 52,000 acres, destroyed 783 buildings, and killed six people. The 2018 Camp Fire, which reduced 10,000 homes to ashes and killed 85 people, was also started by a power line.
California’s Power Line Problem
Why is California bearing the brunt of power line-sparked blazes? There are several reasons. Besides the drought that has plagued the state, environmental policy in California has sharply curtailed logging, removal of dead trees, and controlled burns. Meanwhile, the state’s green energy mandate has placed pressure on the state’s largest utility company, Pacific Gas and Electric (PG&E), to ensure California is powered exclusively by renewable energy by 2045. The green energy mandate has turned the company’s attention and resources away from the power grid and to wind and solar.
The green energy mandate by itself is an admirable goal, but there’s a catch – the age of California’s power lines. Most of the Golden State’s towers were built prior to 1950, and these old lines are the most likely to spark fires. The Camp Fire was caused by equipment dating back to 1921. PG&E knew the lines were old, but they were focused more heavily on renewables. In 2018, PG&E spent $2.4 billion on renewables; in 2017, it spent only $1.4 billion on existing infrastructure (e.g. disabling old power lines).
Currently, PG&E is facing bankruptcy due to a series of lawsuits and has no workable plan to fix the state’s aging grid. Meanwhile, due to the frequency and severity of California’s wildfires, the California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) is investigating PG&E power line safety practices and considering breaking the company into smaller entities to allow for more management accountability for power line maintenance.
What About Burying Power Lines?
There is a growing demand from many Californians for utilities to bury more power lines, especially in heavily forested areas. However, this can be prohibitively expensive. Undergrounding can cost up to $5 million a mile – at that price, it would cost PG&E over $100 billion to underground all of its high-power lines. Additionally, there is concern about digging in environmentally fragile or protected areas.
How Energy Storage Expansion Could Help
The best solution to prevent another devastating fire may be for California to shut down aging power lines. But how will the state ensure that it has enough energy to disable lines and avoid blackouts? That’s where energy storage comes in. Energy storage is the process of storing renewable energy (like wind or solar), since it is not always available in nature. It allows buildings to lower their demand from the grid during peak times when electricity becomes more expensive and keeps prices low by allowing distributors to purchase electricity during cheaper off-peak times.
With the recent energy shortage crisis in California, elected officials have become increasingly aware of the necessity of grid resilience. Energy storage provides resilience because it serves as a backup supply of energy if power generation is interrupted. An increase in energy storage installations across the state would expand the capacity of existing and future renewables, thereby helping California transition away from the remainder of electricity it still sends across transmission lines. The more lines are removed or disabled, the less chance there will be of one sparking a fire.
How Can EnergyWatch Assist with Energy Storage?
EnergyWatch’s energy management platform, Watchwire, allows for easy invoice and meter data acquisition to evaluate and quantify the efficacy of energy storage projects. Watchwire provides: Full visibility into invoice line items and tariff structures, peak load alerts that make it possible to determine when to initiate energy storage use to limit demand from the grid, and analysis of energy storage projects and measurement & verification once they are implemented. To learn more about how Watchwire can help in your energy storage projects, download the full solution brief.
 Top Sustainability Trends to Watch in 2025
Top Sustainability Trends to Watch in 2025

 Log In
Log In